Everything About Robotic Knee Replacement
A robotic knee replacement is similar to a standard knee replacement in that it replaces the knee joint. Damaged tissue in your knee is removed and replaced with an artificial joint by your surgeon. The only difference is that it’s made with the help of a robotic arm.
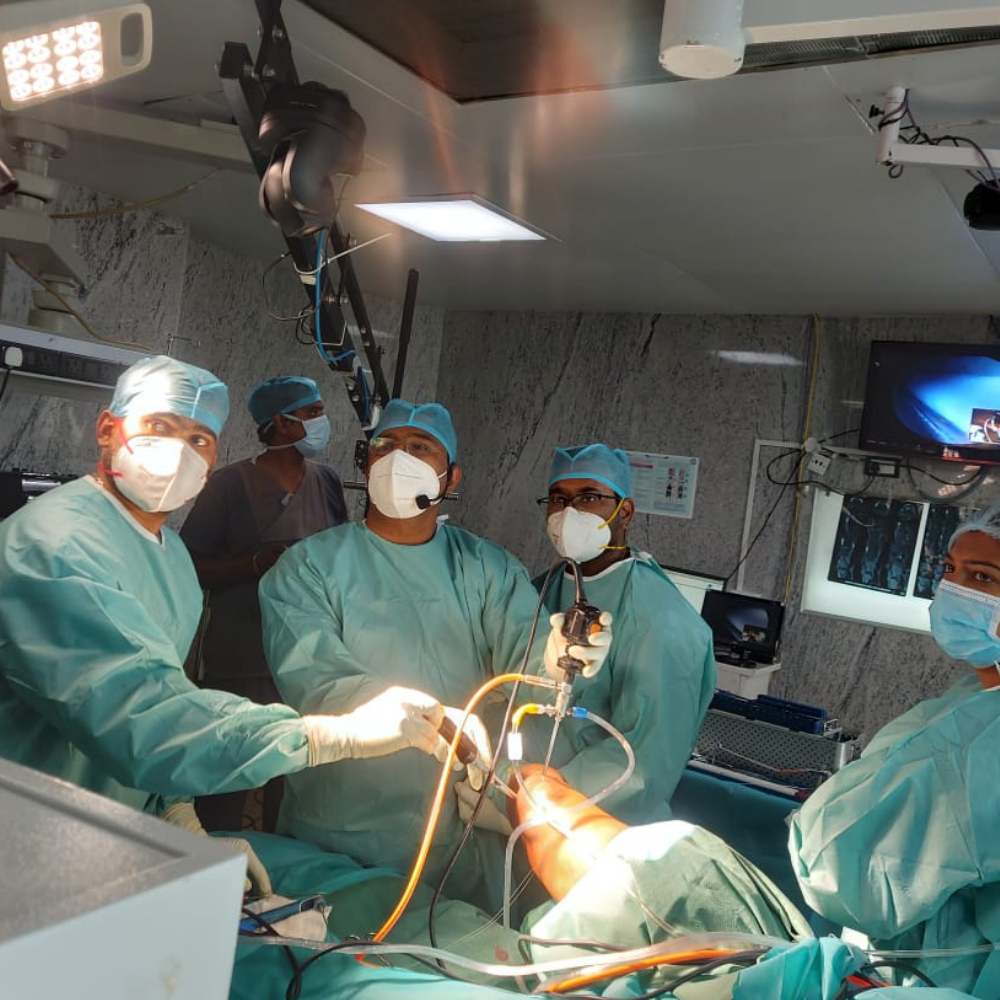
Everything About Robotic Total Knee Replacement and its Treatment
A robotic knee replacement is similar to a standard knee replacement in that it replaces the knee joint. Damaged tissue in your knee is removed and replaced with an artificial joint by your surgeon. The only difference is that it's made with the help of a robotic arm.
Table Of Index
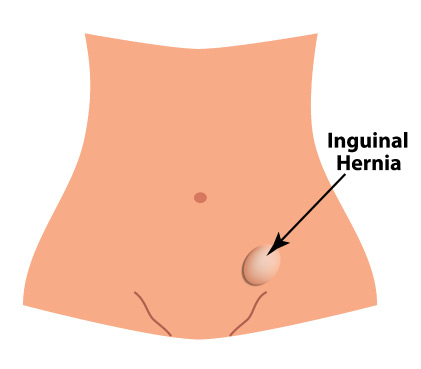
What is Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia is a type of hernia that occurs when abdominal contents, such as fat or part of the intestine, protrude through a weak spot in the abdominal wall near the groin. This can cause a bulge in the groin area, which may be painful or uncomfortable. Inguinal hernias are more common in men than in women, and they can occur at any age. Treatment for an inguinal hernia often involves surgery to repair the weakened area of the abdominal wall and prevent the hernia from getting worse.
What is Inguinal Hernia?
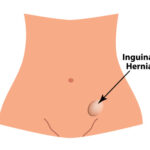
An inguinal hernia is a type of hernia that occurs when abdominal contents, such as fat or part of the intestine, protrude through a weak spot in the abdominal wall near the groin. This can cause a bulge in the groin area, which may be painful or uncomfortable. Inguinal hernias are more common in men than in women, and they can occur at any age. Treatment for an inguinal hernia often involves surgery to repair the weakened area of the abdominal wall and prevent the hernia from getting worse.
Why Does it Happen?
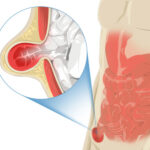
When abdominal tissues or organs press through a weak area in the inguinal canal, an inguinal hernia, also known as a groin hernia, results. Males who have an improperly closed opening between their testicles and abdomen are more likely to develop this sort of hernia. The barrier usually closes soon after the baby is born. However, a partially open opening reduces the strength of the muscular wall and results in a weak area. A bulge begins to form when the tissues press on the weak spot, which may or may not initially create any symptoms. But symptoms will start to show as the bulge pushes the muscle wall and makes a hole.
Why Does it Happen?
When abdominal tissues or organs press through a weak area in the inguinal canal, an inguinal hernia, also known as a groin hernia, results. Males who have an improperly closed opening between their testicles and abdomen are more likely to develop this sort of hernia. The barrier usually closes soon after the baby is born. However, a partially open opening reduces the strength of the muscular wall and results in a weak area. A bulge begins to form when the tissues press on the weak spot, which may or may not initially create any symptoms. But symptoms will start to show as the bulge pushes the muscle wall and makes a hole.

Recovery Rate
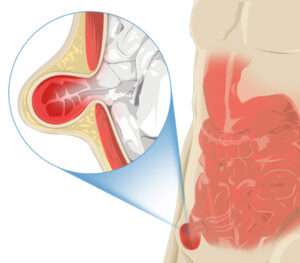
The majority of inguinal hernia repair procedures are day care surgeries, allowing you to go home the same day as your procedure. You must, however, refrain from engaging in any vigorous exercise for at least six weeks. Following hernia repair surgery, you can gradually resume weight-bearing activities six to eight weeks after the procedure. Depending on how physically demanding your job is, you may or may not be able to return to it at this time. Speak to your surgeon or doctor if you are unsure. In order to lower the possibility of your inguinal hernia returning, it's crucial to give your body ample time to heal. Keyhole inguinal hernia repair surgery typically results in a quicker recovery; you might be able to drive after just one week. To prevent hurting yourself before your body has had a chance to heal properly, you should always see your surgeon or doctor.
Recovery Rate

The majority of inguinal hernia repair procedures are day care surgeries, allowing you to go home the same day as your procedure. You must, however, refrain from engaging in any vigorous exercise for at least six weeks. Following hernia repair surgery, you can gradually resume weight-bearing activities six to eight weeks after the procedure. Depending on how physically demanding your job is, you may or may not be able to return to it at this time. Speak to your surgeon or doctor if you are unsure. In order to lower the possibility of your inguinal hernia returning, it's crucial to give your body ample time to heal. Keyhole inguinal hernia repair surgery typically results in a quicker recovery; you might be able to drive after just one week. To prevent hurting yourself before your body has had a chance to heal properly, you should always see your surgeon or doctor.
Causes
- Excess abdominal muscle wall pressure
- Earlier present weak area in the inguinal canal wall
- straining while going to the bathroom
- workout or physical activity that is difficult
- persistent sneezing or coughing
Symptoms
The main symptoms of an inguinal hernia include:
- A bulge or lump in the groin or abdomen. This is the most common symptom of an inguinal hernia, and it is usually more noticeable when standing or coughing.
- Pain or discomfort in the groin or abdomen. This can range from a dull ache to a sharp pain, and it is often worse when lifting heavy objects or straining.
- A feeling of weakness or heaviness in the groin or abdomen. Some people with inguinal hernias may feel like something is dragging or pulling in their groin area.
- A burning or aching sensation in the groin or abdomen.
Causes
- Excess abdominal muscle wall pressure
- Earlier present weak area in the inguinal canal wall
- straining while going to the bathroom
- workout or physical activity that is difficult
- persistent sneezing or coughing
Symptoms
The main symptoms of an inguinal hernia include:
- A bulge or lump in the groin or abdomen. This is the most common symptom of an inguinal hernia, and it is usually more noticeable when standing or coughing.
- Pain or discomfort in the groin or abdomen. This can range from a dull ache to a sharp pain, and it is often worse when lifting heavy objects or straining.
- A feeling of weakness or heaviness in the groin or abdomen. Some people with inguinal hernias may feel like something is dragging or pulling in their groin area.
- A burning or aching sensation in the groin or abdomen.
Diagnosis
Depending on the symptoms and the severity of the hernia, the doctor may do specific tests if a patient seeks medical attention for a hernia. Typically, a doctor may identify a hernia with just a physical examination. However, the doctor may order an imaging test like an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI in some circumstances where the diagnosis isn’t immediately clear.
Although hernias in and around the belly or groyne area are the most prevalent types of hernias, a hernia can affect other sections of the body in different ways. One may not experience any pain or discomfort in the early stages, but they may notice a lump or swelling in and around the abdomen’s affected areas. While coughing, standing up, or sitting down, the lump or swelling will be very noticeable, but once the person is lying down, the lump or swelling may go away or get smaller.
To check for infections, the doctor might recommend blood testing.
When a youngster exhibits sleep apnea symptoms, they may be instructed to spend the night in the hospital. Electrodes are used by the doctor to track the patients’ respiration and brain activity. Although it is completely painless, some kids may find it challenging to sleep in an unfamiliar location.
Diagnosis
Depending on the symptoms and the severity of the hernia, the doctor may do specific tests if a patient seeks medical attention for a hernia. Typically, a doctor may identify a hernia with just a physical examination. However, the doctor may order an imaging test like an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI in some circumstances where the diagnosis isn’t immediately clear.
Although hernias in and around the belly or groyne area are the most prevalent types of hernias, a hernia can affect other sections of the body in different ways. One may not experience any pain or discomfort in the early stages, but they may notice a lump or swelling in and around the abdomen’s affected areas. While coughing, standing up, or sitting down, the lump or swelling will be very noticeable, but once the person is lying down, the lump or swelling may go away or get smaller.
To check for infections, the doctor might recommend blood testing.
When a youngster exhibits sleep apnea symptoms, they may be instructed to spend the night in the hospital. Electrodes are used by the doctor to track the patients’ respiration and brain activity. Although it is completely painless, some kids may find it challenging to sleep in an unfamiliar location.
Severity
Early-stage inguinal hernias can be controlled by limiting the patient’s physical activity. The illness worsens as time goes on and develops symptoms like-
difficulty walking and climbing stairs, as well as other fundamental tasks.
Pain that is intermittent (sometimes stay for a long period)
It is impossible to shove the hernia back inside.
Symptomatic hernias are typically severe, so it is best to get medical attention right once to stop them from getting worse.
Severity
Early-stage inguinal hernias can be controlled by limiting the patient’s physical activity. The illness worsens as time goes on and develops symptoms like-
difficulty walking and climbing stairs, as well as other fundamental tasks.
Pain that is intermittent (sometimes stay for a long period)
It is impossible to shove the hernia back inside.
Symptomatic hernias are typically severe, so it is best to get medical attention right once to stop them from getting worse.
Risks & Complications
Several issues could arise during a hernia repair procedure. The following general dangers can occur after surgical hernia removal, but they are uncommon:
reaction to anaesthesia
the wound becoming infected
Clots of blood
urethral tract damage
Even after inguinal hernia surgery, there is a potential of post-operative problems for around a month until recovery is complete, including
Infected Mesh
severe pain in the stitches or wound
Seroma or a buildup of fluid
Hematoma or a buildup of blood
infection of a wound
urinary incontinence
Recurrence
The doctor provides a thorough recovery plan with specific advice on what to do and not do following inguinal hernia repair surgery in order to prevent these issues.
Untreated hernias can block muscles from the inside, blocking blood flow to the tissues and increasing the risk of life-threatening complications like strangulation or imprisonment. A person may also experience symptoms including nausea, a persistent fever, blood in the faeces, vomiting, stomach pain, and a sharp lump in the groyne when the intestine becomes caught in the inguinal canal. These situations pose a risk to life and are regarded as medical emergencies.
Risks & Complications
Several issues could arise during a hernia repair procedure. The following general dangers can occur after surgical hernia removal, but they are uncommon:
reaction to anaesthesia
the wound becoming infected
Clots of blood
urethral tract damage
Even after inguinal hernia surgery, there is a potential of post-operative problems for around a month until recovery is complete, including
Infected Mesh
severe pain in the stitches or wound
Seroma or a buildup of fluid
Hematoma or a buildup of blood
infection of a wound
urinary incontinence
Recurrence
The doctor provides a thorough recovery plan with specific advice on what to do and not do following inguinal hernia repair surgery in order to prevent these issues.
Untreated hernias can block muscles from the inside, blocking blood flow to the tissues and increasing the risk of life-threatening complications like strangulation or imprisonment. A person may also experience symptoms including nausea, a persistent fever, blood in the faeces, vomiting, stomach pain, and a sharp lump in the groyne when the intestine becomes caught in the inguinal canal. These situations pose a risk to life and are regarded as medical emergencies.

Keeping a healthy body weight is essential for avoiding the formation of a hernia because an obese person is more prone to get one. Including high-fiber foods in one’s diet, quitting smoking, treating chronic coughing and sneezing properly, and employing proper lifting techniques are a few other measures to avoid having a hernia.

Keeping a healthy body weight is essential for avoiding the formation of a hernia because an obese person is more prone to get one. Including high-fiber foods in one’s diet, quitting smoking, treating chronic coughing and sneezing properly, and employing proper lifting techniques are a few other measures to avoid having a hernia.
Our Services
Our Services
When to consult a doctor ?
Consult your surgeon as soon as you experience :
We advise consulting a hernia expert or your health care physician. if you feel pain or a protrusion in your abdominal or groyne.
Your doctor can examine you and provide you guidance on the best course of action.
Our Specialist

***
When to consult a doctor ?
Consult your surgeon as soon as you experience :
We advise consulting a hernia expert or your health care physician. if you feel pain or a protrusion in your abdominal or groyne.
Your doctor can examine you and provide you guidance on the best course of action.
Our Specialist

Dr. Adithya V Naragund
Director of Gastrosciences & Soft Tissue Robotic Surgeon

Dr. Shashikiran N J
Minimal Access Thoracic, Gastrointestinal and General Surgery

***
Testimonials
AASRA Patients Review

Insurance coverage
Insurance does cover the cost of the surgical procedure for a hysterectomy performed due to adenomyosis because it is on the list of procedures that are "medically required." The cost capping, however, may change from instance to case. Please get your healthcare or insurance company to validate this.
Insurance coverage

Insurance does cover the cost of the surgical procedure for a hysterectomy performed due to adenomyosis because it is on the list of procedures that are "medically required." The cost capping, however, may change from instance to case. Please get your healthcare or insurance company to validate this.
Frequently Asked Questions
An inguinal hernia is a type of hernia that occurs when abdominal contents, such as fat or part of the intestine, protrude through a weak spot in the abdominal wall near the groin. This can cause a bulge in the groin area, which may be painful or uncomfortable. Inguinal hernias are more common in men than in women, and they can occur at any age. Treatment for an inguinal hernia often involves surgery to repair the weakened area of the abdominal wall and prevent the hernia from getting worse.
No, both men and women can get an inguinal hernia. However, men are much more likely to get them than women are; a woman's lifetime risk of getting an inguinal hernia is only 3.5-8%, whereas a man's risk is 27-42%. The difference is due to differences in anatomy.
When abdominal tissue presses through the inguinal canal in your abdominal wall, it causes an inguinal hernia. As a result, an inguinal hernia is more likely to occur if your abdominal wall is weak. This region of the abdominal wall is particularly vulnerable to weakening in men because more tissues, specifically the spermatic cord that attaches to the testes, travel through the inguinal canal.
Inguinal hernias are most common in men, and they tend to occur when people are between the ages of 30 and 60. However, inguinal hernias can also occur in infants and young children. In general, inguinal hernias are more common in people who are older, and they are also more common in people who have certain risk factors, such as a family history of hernias or conditions that increase abdominal pressure, such as chronic cough or constipation or urinary difficulty.
The main risk factors for developing an inguinal hernia include:
- Age: Inguinal hernias are more common in older people, especially those between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Gender: Inguinal hernias are more common in men than in women.
- Family history: If you have a family history of inguinal hernias, you may be at an increased risk of developing one.
- Chronic cough, constipation or urinary difficulty: Conditions that increase abdominal pressure can increase your risk of developing an inguinal hernia.
- Previous surgery: If you have had previous abdominal surgery, you may be at an increased risk of developing an inguinal hernia.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing an inguinal hernia.
It's important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean that you will definitely develop an inguinal hernia. Additionally, some people who develop inguinal hernias may not have any of these risk factors.
Yes, if you've been a smoker for a while. This is due to the fact that smoking raises your risk of contracting COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), a lung condition that results in a persistent cough. Your stomach and groin muscles will be put under more stress as a result. Smoking also impairs wound healing and results in hernia.
Depending on your overall risk for the ailment, lifting heavy objects or engaging in intense activity can cause an inguinal hernia. Not everyone who routinely lifts heavy weights will get an inguinal hernia, although it is more likely if you have multiple risk factors for the ailment. For instance, if COPD, BPH, or another ailment weakens or strains your abdominal wall, or if inguinal hernias run in your family, you've had prior surgery in the groin area.
You have a higher risk of developing an inguinal hernia if you have chronic constipation, defined as constipation that lasts for many months or more. This is because having a constipation makes it harder for you to open your bowels, which puts additional tension on your groin and abdominal muscles.
The main symptoms of an inguinal hernia include:
- A bulge or lump in the groin or abdomen. This is the most common symptom of an inguinal hernia, and it is usually more noticeable when standing or coughing.
- Pain or discomfort in the groin or abdomen. This can range from a dull ache to a sharp pain, and it is often worse when lifting heavy objects or straining.
- A feeling of weakness or heaviness in the groin or abdomen. Some people with inguinal hernias may feel like something is dragging or pulling in their groin area.
- A burning or aching sensation in the groin or abdomen.
It's important to note that not everyone with an inguinal hernia will have all of these symptoms, and some people may have no symptoms at all. If you have any concerns about a potential hernia, you should talk to your doctor. They can perform an examination to determine whether you have a hernia and recommend treatment if necessary.
Inguinal hernias do not get better on their own, and they can often worsen over time. If you have an inguinal hernia, it is important to see a doctor and discuss your treatment options. In most cases, inguinal hernias will require surgical repair to prevent complications, such as strangulation or obstruction of the intestine. If you have an inguinal hernia and you are experiencing pain or discomfort, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Delaying treatment can increase the risk of complications and may make the hernia more difficult to repair.
Inguinal hernias can progress in several ways. In some cases, an inguinal hernia may remain small and cause no symptoms. However, if the hernia is left untreated, it can become larger and more noticeable. This can cause discomfort and pain, and it can make it difficult to engage in physical activity. In some cases, an inguinal hernia can become trapped or incarcerated, which means that the intestine or other abdominal tissue has become stuck in the hernia and cannot be pushed back into the abdomen. This can be a medical emergency, as it can cause the blood supply to the trapped tissue to be cut off. If this occurs, it can lead to strangulation or gangrene, which can be life-threatening. For these reasons, it is important to see a doctor if you think you have an inguinal hernia, and to follow their recommended treatment plan. This can help to prevent the hernia from worsening and avoid complications.
Get In Touch
Mailing Address
No. 9, TKN Towers, Tilak Nagar, Jayanagar, Bannerughatta Main Road, Bengluru – 560041
Email Address
Phone Number
080 – 2399 9999
Get In Touch
Mailing Address
No. 9, TKN Towers, Tilak Nagar, Jayanagar, Bannerughatta Main Road, Bengluru – 560041
Email Address
Phone Number
080 – 2399 9999