Everything About Robotic Knee Replacement
A robotic knee replacement is similar to a standard knee replacement in that it replaces the knee joint. Damaged tissue in your knee is removed and replaced with an artificial joint by your surgeon. The only difference is that it’s made with the help of a robotic arm.
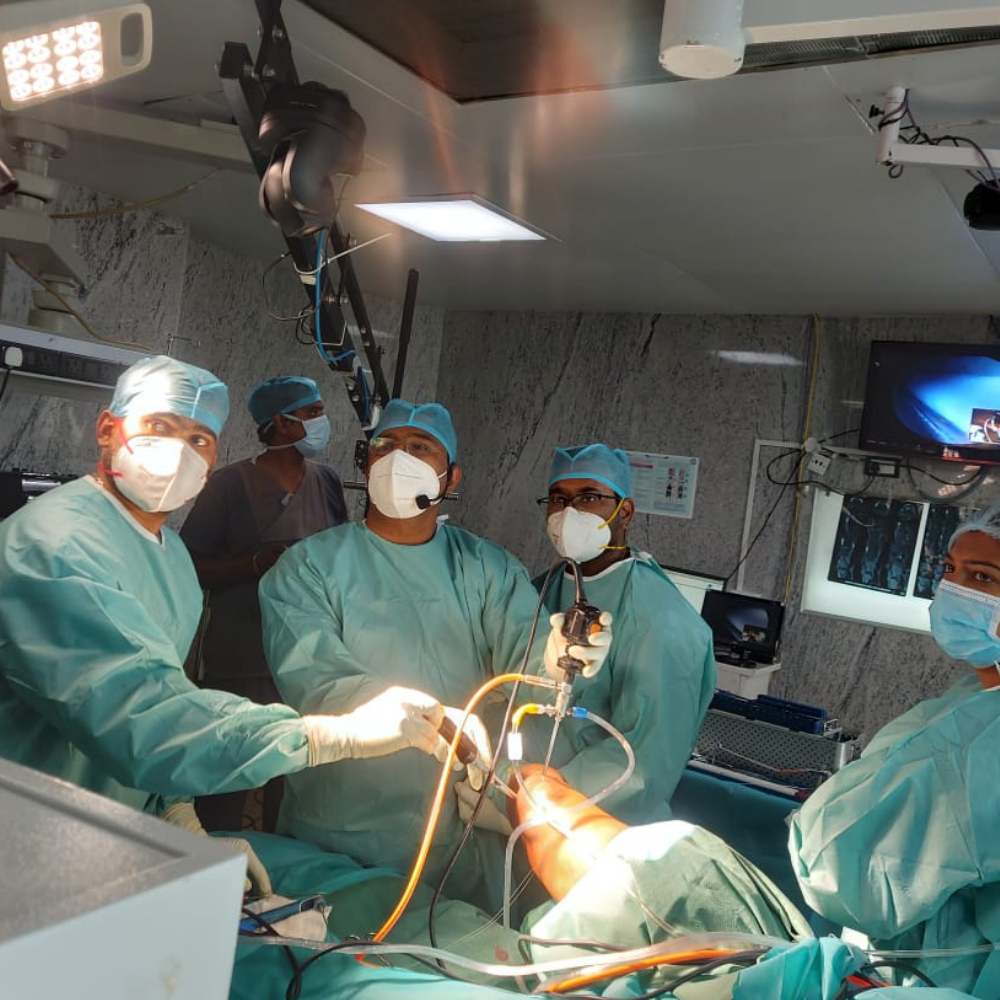
Everything About Robotic Total Knee Replacement and its Treatment
A robotic knee replacement is similar to a standard knee replacement in that it replaces the knee joint. Damaged tissue in your knee is removed and replaced with an artificial joint by your surgeon. The only difference is that it's made with the help of a robotic arm.
What is Liver Disease?
Liver resections for Cancers of the liver/ bile ducts or Colorectal Liver metastases can be performed by Robotic and Laparoscopic techniques as well. Patient selection is vital to outcomes and we use advanced imaging techniques to identify resectability before embarking on these procedures.
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
- This procedure is done in case of rotator cuff injuries following fall with injury to shoulder and sports injuries
- The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia.
- Tendons are reattached to bone (head of arm bone) using rivets known as suture anchors under the vision of arthroscope.
- They may be metal or bio absorbable and need not be removed, with sutures attached to them for tying the tendons.
- After surgery rehabilitation is started after 2 weeks and graduated physiotherapy is done for 2 months.
Arthroscopic assisted Latarjet
- This procedure is done in patients having recurrent shoulder dislocation.
- This procedure is usually done under general anaesthesia.
- Capsule is reattached to bone (shoulder blade) using rivets known as suture anchors under the vision of arthroscope.
- After surgery rehabilitation is started after 2 weeks and graduated physiotherapy is done for 2 months.
What is Pancreatic Disease?
The pancreas is inflamed by pancreatitis. The pancreas is a long, flat gland that is hidden in the upper belly beyond the stomach. The pancreas creates hormones that regulate how your body handles sugar and enzymes that aid in digestion (glucose).
Acute pancreatitis, which manifests rapidly and lasts for days, is one type of pancreatitis that can happen. Chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatitis that lasts for a long time, can occur in some persons.
Arthroscopic AC joint repair
- This procedure is done in patients with dislocation of joint between clavicle (collar bone) and acromion (projection of shoulder blade).
- This procedure is usually done under general anaesthesia
- 2 or 3 very small incisions are made. A separate 2cm mini-open incision is made over collar bone to complete fixation.
- Strong fibre-tape passed through a small drill hole in collar bone and coracoid process of shoulder blade.
- The tapes are looped and tightened over small titanium button, which pull the collar bone down to its correct position.
- The tape holds the joint in correct place while the injured ligaments heal.
- After surgery rehabilitation is started after 2 weeks and graduated physiotherapy is done for 2 months.
Arthroscopic frozen shoulder release
- This procedure is done in patients with stiff shoulder/ frozen shoulder.
- This procedure is usually done under general anaesthesia.
- An area at the front of the shoulder called rotator interval is completely cleared of inflamed thickened capsule.
- Anterior and superior part of capsule is released (like perforations on a piece of paper).
- This may be accompanied with manipulation/passive mobilisation of shoulder.
- After surgery physiotherapy for shoulder mobilisation is started from next day.

Recovery Rate
Recovery may require one to six months. For the first week, you'll probably have to wear a sling. You might need to wear the sling for a longer period if you had extensive repairs made. To manage your pain, you may take medication.
Arthroscopic Bankart repair
- This procedure is done in patients with recurrent shoulder dislocation with bony defect of the shoulder blade and/or head of arm bone.
- This procedure is usually done under general anesthesia
- Part of the Coracoid process (bony projection) present over the front of the shoulder blade is taken and passed through the Subscapularis muscle by splitting it.
- It is fixed to the front of the shoulder near the neck of the shoulder blade with screws to repair the bony defect causing instability.
- After surgery rehabilitation is started after 2 weeks and graduated physiotherapy is done for 2 months
Arthroscopic AC joint repair
- This procedure is done in patients with dislocation of joint between clavicle (collar bone) and acromion (projection of shoulder blade).
- This procedure is usually done under general anaesthesia
- 2 or 3 very small incisions are made. A separate 2cm mini-open incision is made over collar bone to complete fixation.
- Strong fibre-tape passed through a small drill hole in collar bone and coracoid process of shoulder blade.
- The tapes are looped and tightened over small titanium button, which pull the collar bone down to its correct position.
- The tape holds the joint in correct place while the injured ligaments heal.
- After surgery rehabilitation is started after 2 weeks and graduated physiotherapy is done for 2 months.
Arthroscopic frozen shoulder release
- This procedure is done in patients with stiff shoulder/ frozen shoulder.
- This procedure is usually done under general anaesthesia.
- An area at the front of the shoulder called rotator interval is completely cleared of inflamed thickened capsule.
- Anterior and superior part of capsule is released (like perforations on a piece of paper).
- This may be accompanied with manipulation/passive mobilisation of shoulder.
- After surgery physiotherapy for shoulder mobilisation is started from next day.
Recovery Rate

Recovery may require one to six months. For the first week, you'll probably have to wear a sling. You might need to wear the sling for a longer period if you had extensive repairs made. To manage your pain, you may take medication
Causes
- Arthritis.
- Cartilage injury.
- Rotator cuff injury.
- Swollen tendons or bursa sacs.
- Bone growths (bony projections that develop along the edges of bones)
- Shoulder or neck pinched nerve.
- Fractured arm or shoulder bone.
- Fractured arm or shoulder bone. shoulder.
Symptoms
- Radiating shoulder pain.
- Sleepless nights due to pain.
- Weakness in the affected arm.
- Pain continues without physical activity.
- Lifting and reaching are impaired.
Causes
- Arthritis.
- Cartilage injury.
- Rotator cuff injury.
- Swollen tendons or bursa sacs.
- Bone growths (bony projections that develop along the edges of bones)
- Shoulder or neck pinched nerve.
- Fractured arm or shoulder bone.
- Fractured arm or shoulder bone. shoulder.
Symptoms
- Radiating shoulder pain.
- Sleepless nights due to pain.
- Weakness in the affected arm.
- Pain continues without physical activity.
- Lifting and reaching are impaired.
Diagnosis
A doctor can identify a rotator cuff injury by looking through the patient’s medical history, conducting a complete physical examination, checking the patient’s shoulder, and using imaging methods including X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The physical examination and medical history are trustworthy tools for identifying rotator cuff discomfort and weakening. The cuff cannot be seen on an X-ray, therefore people frequently have no anomalies, but an MRI is quite reliable in confirming a suspected diagnosis. A MRI arthrogram will frequently be carried out. Just before the MRI, a contrast “dye” is injected into the joint for this investigation. The diagnosis of a tear using this technique is almost 100% correct.
X-rays may reveal bone damage as a result of a torn rotator cuff that is not functioning properly. On rare occasions, cysts can be seen where the cuff attaches to the humerus, the humeral head may move in the direction of the acromial roof, or bone spurs may form on the underside of this roof. MRI scans show the rotator cuff in cross-section. Large and huge tears are immediately discernible, but small, delicate tears or fraying of the cuff tissue are frequently observed.
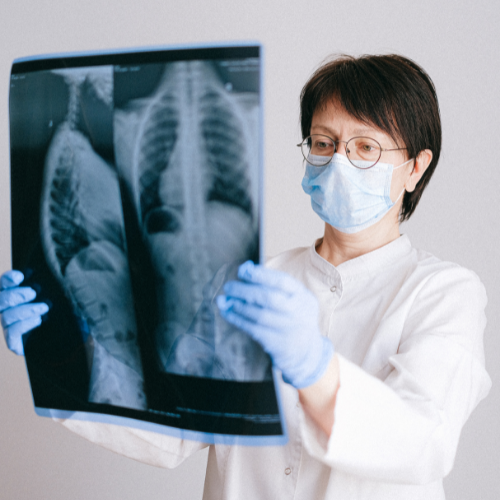
Diagnosis
A doctor can identify a rotator cuff injury by looking through the patient’s medical history, conducting a complete physical examination, checking the patient’s shoulder, and using imaging methods including X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The physical examination and medical history are trustworthy tools for identifying rotator cuff discomfort and weakening. The cuff cannot be seen on an X-ray, therefore people frequently have no anomalies, but an MRI is quite reliable in confirming a suspected diagnosis. A MRI arthrogram will frequently be carried out. Just before the MRI, a contrast “dye” is injected into the joint for this investigation. The diagnosis of a tear using this technique is almost 100% correct.
X-rays may reveal bone damage as a result of a torn rotator cuff that is not functioning properly. On rare occasions, cysts can be seen where the cuff attaches to the humerus, the humeral head may move in the direction of the acromial roof, or bone spurs may form on the underside of this roof. MRI scans show the rotator cuff in cross-section. Large and huge tears are immediately discernible, but small, delicate tears or fraying of the cuff tissue are frequently observed.
Risks & Complications
- medication adverse response allergies
- Breathing problems
- Infection, bleeding, and blood clots
- Stiff shoulders
- Surgery’s failure to treat symptoms
- The fix does not hold up.
- Instability in the shoulder
- Injury to a blood vessel or nerve
- Damage to the shoulder’s cartilage (chondrolysis)
Benefits of Advanced Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Accuracy in diagnosis
- A danger of problems such as an infection or a blood clot in the joint is less than 1%.
- Only one or two days are spent in the hospital, and recovery time at home is quick.
- Following surgery, physiotherapy can be started right away, hastening recovery.
- Compared to traditional surgery, recovery time is substantially quicker.
Benefits of Advanced Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Accuracy in diagnosis
- A danger of problems such as an infection or a blood clot in the joint is less than 1%.
- Only one or two days are spent in the hospital, and recovery time at home is quick.
- Following surgery, physiotherapy can be started right away, hastening recovery.
- Compared to traditional surgery, recovery time is substantially quicker.
Risks & Complications
- medication adverse response allergies
- Breathing problems
- Infection, bleeding, and blood clots
- Stiff shoulders
- Surgery’s failure to treat symptoms
- The fix does not hold up.
- Instability in the shoulder
- Injury to a blood vessel or nerve
- Damage to the shoulder’s cartilage (chondrolysis)
When to consult a doctor ?
Consult your surgeon as soon as you experience :
In order to determine whether GI and HPB surgery is right for them, a person may have symptoms from conditions like:
- Stomach pain and inflammation
- Gastrointestinal or duodenal
- H. pylori infection.
- Disease of gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
- Stomach ulcers (sores)
Our Specialist

***
When to consult a doctor ?
Consult your surgeon as soon as you experience :
In order to determine whether GI and HPB surgery is right for them, a person may have symptoms from conditions like:
- Stomach pain and inflammation
- Gastrointestinal or duodenal
- H. pylori infection.
- Disease of gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
- Stomach ulcers (sores)
Our Specialist

***

Insurance coverage
Insurance does cover the cost of the surgical procedure for a hysterectomy performed due to adenomyosis because it is on the list of procedures that are "medically required." The cost capping, however, may change from instance to case. Please get your healthcare or insurance company to validate this.
Insurance coverage

Insurance does cover the cost of the surgical procedure for a hysterectomy performed due to adenomyosis because it is on the list of procedures that are "medically required." The cost capping, however, may change from instance to case. Please get your healthcare or insurance company to validate this.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Facts and figures around robotic hip replacement
Why choose Aasra for robotic knee replacement treatment?
AASRA Hospital has the state of the art technology for performing joint replacement surgeries i,e MAKO Robitic joint replacement technology.
There is less post operative pain, reduced hospital stay ,patient can walk early and early recovery .
How to book appointment for aasra
Booking an appointment with a Aasra Orthopedician is easy.
Simply give us a call directly or complete our online appointment booking form. The only four questions it would ask you are “Your name,” “Contact,” and “tell us a little more about yourself.” Simply complete the form and press “submit.” One of our medical coordinators will give you a call soon to assist you in speaking with the doctor of your choice.
Facts and figures around robotic hip replacement
Why choose Aasra for robotic hip replacement treatment?
AASRA Hospital has the state of the art technology for performing joint replacement surgeries i,e MAKO Robitic joint replacement technology.
There is less post operative pain, reduced hospital stay ,patient can walk early and early recovery .
How to book an appointment for aasra?
Booking an appointment with a Aasra Orthopedician is easy.
Simply give us a call directly or complete our online appointment booking form. The only four questions it would ask you are “Your name,” “Contact,” and “tell us a little more about yourself.” Simply complete the form and press “submit.” One of our medical coordinators will give you a call soon to assist you in speaking with the doctor of your choice.
